
|Q1 What is CE marking?

CE marking signifies that the manufacturer of a product certifies that the product meets all essential requirements of applicable EC directives. (It is necessary to conform to the requirements of all applicable EC directives.) “CE” is an abbreviation of Communauté Européenne (French) (European Community in English).
|Q2 What are EC Directives and EN Standards?
 In the past, each EU member country established its own standards in order to guarantee product quality and safety. Today, EC directives constitute standards common to all member countries and facilitate free distribution of goods within the EU. (Written decisions of the Council of Ministers of the European Community are called EC directives.) Standards established by the European standardization bodies CEN and CENELEC are EN standards. Among EN standards, harmonized standards, established via procedures and consensus, contain more specific requirements for complying with the EC directives. EN standards complement EC directives.
In the past, each EU member country established its own standards in order to guarantee product quality and safety. Today, EC directives constitute standards common to all member countries and facilitate free distribution of goods within the EU. (Written decisions of the Council of Ministers of the European Community are called EC directives.) Standards established by the European standardization bodies CEN and CENELEC are EN standards. Among EN standards, harmonized standards, established via procedures and consensus, contain more specific requirements for complying with the EC directives. EN standards complement EC directives.
|Q3 What happens in the case of devices without CE marking?
 Products/devices to be exported to (or distributed in) EU member countries are required to conform to EC directives. Without CE marking showing conformity, they cannot be distributed in EU member countries.
Products/devices to be exported to (or distributed in) EU member countries are required to conform to EC directives. Without CE marking showing conformity, they cannot be distributed in EU member countries.
|Q4 What is the responsibility of the manufacturer in regard to affixing CE marking?
 Because CE marking is a certification by a manufacturer that the product conforms to EC directives, the manufacturer is responsible for affixing a mark. Because the mark is affixed based on the manufacturer’s declaration, if there is a safety problem with a product or device bearing the CE mark and the product has been properly used, or if nonconformity with EC directives is determined, the relevant EU member country may take appropriate action. It can restrict free movement of the product or equipment, remove it from the market, prohibit shipment, operation and use, and more.
Because CE marking is a certification by a manufacturer that the product conforms to EC directives, the manufacturer is responsible for affixing a mark. Because the mark is affixed based on the manufacturer’s declaration, if there is a safety problem with a product or device bearing the CE mark and the product has been properly used, or if nonconformity with EC directives is determined, the relevant EU member country may take appropriate action. It can restrict free movement of the product or equipment, remove it from the market, prohibit shipment, operation and use, and more.
|Q5 How are manufacturers exporting to EU countries responding to these requirements?
What is the trend?
 In order to avoid the risks mentioned in A4 above, manufacturers are increasingly asking third-party testing organizations, including EC Notified Bodies, to conduct inspections/tests and are obtaining certifications of conformity (certification is done only by an EC Notified Body), before affixing CE marking.
In order to avoid the risks mentioned in A4 above, manufacturers are increasingly asking third-party testing organizations, including EC Notified Bodies, to conduct inspections/tests and are obtaining certifications of conformity (certification is done only by an EC Notified Body), before affixing CE marking.
|Q6 What do EC directives cover?
 Of EC directives related to CE marking, the main ones are listed below. Products/devices subject to multiple directives are required to meet all applicable requirements.
Of EC directives related to CE marking, the main ones are listed below. Products/devices subject to multiple directives are required to meet all applicable requirements.
(As of July 2010)
| Directive Name | Directive No. | Major Products |
|---|---|---|
| Machinery | 2006/42/EC | Machine tools, construction machinery, woodworking machinery, SMD placement equipment, testing equipment, textile machinery |
| Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) | 2014/30/EU | Equipment with electrical/electronic components, home appliances, office equipment, telephones, electric motors |
| Low Voltage | 2014/35/EC | Equipment that is designed or adapted for use between 50 and 1000 VAC or between 75 and 1500 VDC |
| Medical Devices | 93/42/EEC | Diagnostic and treatment equipment |
| Simple Pressure Vessels | 2014/29/EU | Gas pressure vessels, compressed air containers for automobile brakes |
| Wireless devices | 2014/53/EU | FAX, modems, ISDN |
| Toy Safety | 2009/142/EC | Dolls, puzzles, children’s bicycles |
| Gas Appliances | 2009/142/EC | Gas heaters, gas water heaters |
| Marking | 93/68/EEC | Consistency of use of CE marking |
| RoHS | 2011/65/EU | Restriction of hazardous substances when disposing of products containing electrical and electronic equipment |
|Q7 What is the Machinery Directive?
 This directive applies to industrial machinery, primarily machine tools, injection molding machines and automated machines, and requires all essential safety items. Pneumatic equipment and / or motorless type actuator is not covered by the Machinery Directive and is not subject to it. However, having the conformity of SMC’s equipment to European standards certified can facilitate the customer’s creation of a technical file (TCF) for its Declaration of Conformity.
This directive applies to industrial machinery, primarily machine tools, injection molding machines and automated machines, and requires all essential safety items. Pneumatic equipment and / or motorless type actuator is not covered by the Machinery Directive and is not subject to it. However, having the conformity of SMC’s equipment to European standards certified can facilitate the customer’s creation of a technical file (TCF) for its Declaration of Conformity. |Q8 What is the Low Voltage Directive?
 This directive applies to equipment with rated voltage between 50 and 1000 VAC or between 75 and 1500 VDC, and requires electrical safety.
This directive applies to equipment with rated voltage between 50 and 1000 VAC or between 75 and 1500 VDC, and requires electrical safety.|Q9 What is the Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive?
 This directive relates to electromagnetic compatibility (EMC), and requires that for equipment with a risk of emitting electromagnetic noise with adverse effects on other equipment, that the emission of excessive electromagnetic noise be prevented, and that for equipment with a risk of being adversely affected by such other equipment, that there be protection from emissions of electromagnetic noise from other equipment (emissions immunity). An example of testing a digital flow switch (PFA PFW) is given below.
This directive relates to electromagnetic compatibility (EMC), and requires that for equipment with a risk of emitting electromagnetic noise with adverse effects on other equipment, that the emission of excessive electromagnetic noise be prevented, and that for equipment with a risk of being adversely affected by such other equipment, that there be protection from emissions of electromagnetic noise from other equipment (emissions immunity). An example of testing a digital flow switch (PFA PFW) is given below.
(As of July 2010)
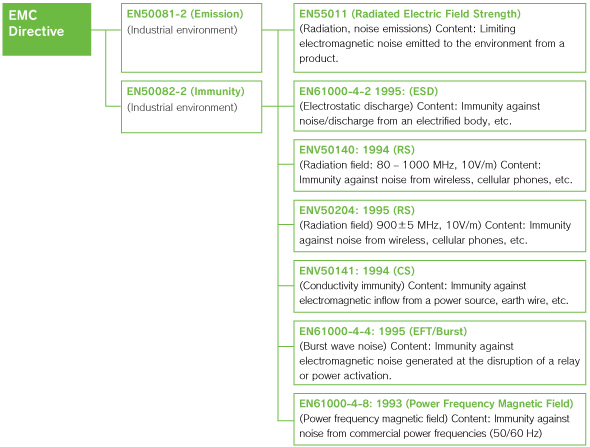 Testing is conducted for each item and if all requirements are satisfied, a product can be deemed to conform to the EMC Directive. SMC obtains certification of conformity to the EMC Directive for each of its product, so that there is no noise nonconformity when the customer obtains certification for the customer’s entire product or device.
Testing is conducted for each item and if all requirements are satisfied, a product can be deemed to conform to the EMC Directive. SMC obtains certification of conformity to the EMC Directive for each of its product, so that there is no noise nonconformity when the customer obtains certification for the customer’s entire product or device.
|Q10 RoHS Directive
 This Directive concerns the restriction of the use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment to be placed on the EU market.
This Directive concerns the restriction of the use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment to be placed on the EU market.
|Q11 What is the Simple Pressure Vessels Directive?
 This directive applies to welded vessels whose maximum operating pressure (PS) x volume (V) product exceeds 50 bar/litre. An EC-type examination is required for pressure vessels subject to the directive, before affixing the CE mark.
This directive applies to welded vessels whose maximum operating pressure (PS) x volume (V) product exceeds 50 bar/litre. An EC-type examination is required for pressure vessels subject to the directive, before affixing the CE mark.
|Q12 What SMC products are subject to EC directives?
What SMC products require CE marking?
 Directives applying to SMC products are the EMC Directive, the Low Voltage Directive, the Simple Pressure Vessels Directive, and RoHS Directive. Pneumatic equipment using electric/electronic parts is subject either to the EMC Directive or the Low Voltage Directive, or both.
Directives applying to SMC products are the EMC Directive, the Low Voltage Directive, the Simple Pressure Vessels Directive, and RoHS Directive. Pneumatic equipment using electric/electronic parts is subject either to the EMC Directive or the Low Voltage Directive, or both.
Subject products require CE marking. In this respect, pneumatic equipment and / or motorless type actuator not using electric/electronic parts does not require CE marking. SMC’s air tank (Series AT) and booster regulator tank (Series VBAT) are subject to the Simple Pressure Vessels Directive. But except for specially ordered VBAT with CE marking, air tanks and booster regulator tanks do not conform to the directive (no CE marking) and cannot be exported to Europe.
|Q13 What is the difference between CE marking and certifying products?
 As described in “Affixing CE Marks and Declarations of Conformity” and “EC Directives and EN Standards” above, certified products are those that have been certified by a certification authority as conforming to EN standards, which complement EC directives. CE-marked products are those such as for which SMC itself makes a declaration that they conform to EC directives, based on a Certificate of Conformity issued by a certification authority. There is no difference in the products themselves.
As described in “Affixing CE Marks and Declarations of Conformity” and “EC Directives and EN Standards” above, certified products are those that have been certified by a certification authority as conforming to EN standards, which complement EC directives. CE-marked products are those such as for which SMC itself makes a declaration that they conform to EC directives, based on a Certificate of Conformity issued by a certification authority. There is no difference in the products themselves.
|Q14 How do EC directives deal with specially ordered products (product number -X)?
 Product numbers of specially ordered products are not registered in a standard product conformity certificate (certification) and are not products in conformity with standards. In case of products custom-made in ways not prescribed in standards (for example, different lengths of lead wires), conformity certification of a standard product can be effectively used by making clear the commonality and points of difference, and by showing construction plans, dimension outline drawings, etc.
Product numbers of specially ordered products are not registered in a standard product conformity certificate (certification) and are not products in conformity with standards. In case of products custom-made in ways not prescribed in standards (for example, different lengths of lead wires), conformity certification of a standard product can be effectively used by making clear the commonality and points of difference, and by showing construction plans, dimension outline drawings, etc.
|Q15 How are spare parts (for maintenance) dealt with?
 The conformity of equipment (products) with CE marking has been confirmed as to the entire system and there is no need to re-conduct conformity tests for spare parts.
The conformity of equipment (products) with CE marking has been confirmed as to the entire system and there is no need to re-conduct conformity tests for spare parts.
|Q16 What is contained in a technical file (TCF)?
 A technical file is necessary to assess and prove that a product is in conformity with applicable EU directives. It contains documents on how requirements are met and what measures were implemented, as well as technical materials necessary to understand the product, including specifications and wiring diagrams. A typical technical file might, as an example, contain the following:
A technical file is necessary to assess and prove that a product is in conformity with applicable EU directives. It contains documents on how requirements are met and what measures were implemented, as well as technical materials necessary to understand the product, including specifications and wiring diagrams. A typical technical file might, as an example, contain the following:
1.General explanation of the device (instruction manual)
2.System block diagram and wiring diagram
3.Explanation and description necessary to understand the device’s work
4.List of standards and safety measures implemented to satisfy requirements of directives
5.Inspections implemented
6.Report on testing
7.Instruction manual (specifications)
Manufacturers are required to retain such documents together with Declarations of Conformity for ten years after discontinuation of production of the product, and submit them by the specified date whenever requested by a regulatory authority.
|Q17 What is the content of a Declaration of Conformity (conformity declaration)?
 A Declaration of Conformity is a document declaring that a product conforms to all requirements of applicable directives, and must include the following:
A Declaration of Conformity is a document declaring that a product conforms to all requirements of applicable directives, and must include the following:
1.Name of manufacturer
2.Address
3.Name of product and number
4.Directives and harmonized standards to which the product conforms
5.Name and address of agent in EU
6.Signature of the party making the declaration
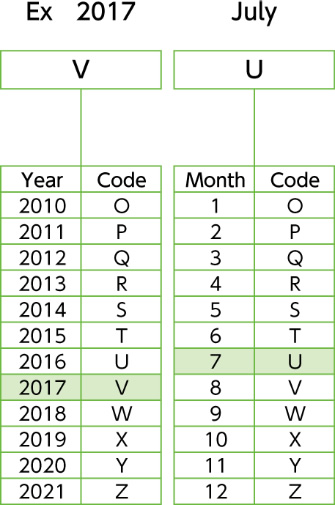
|Q18 Understanding the Production Lot (Batch code)

The chart below shows the meaning of the production lot (batch code)
Typically the code consists of 2 letters. If there is a code with 4 letters, please refer to the first 2 letters.
|Q19 What is the Pressure Equipment Directive?

The Pressure Equipment Directive establishes the guidelines for the design and manufacturing of pressure equipment.
It is applicable to pressure equipment with a maximum allowable pressure that exceeds 0.5 bar.
Products are classified into "vessel", "boiler" or "piping", and the state of the fluid into "gas" or "liquid", and also whether or not it is dangerous.

